Effectively managing and enhancing the quality of life for those with plaque psoriasis requires a deep understanding of this chronic autoimmune disorder, which results in the appearance of raised, red, and scaly patches on the skin. This comprehensive guide offers vital insights from experts regarding the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for plaque psoriasis.
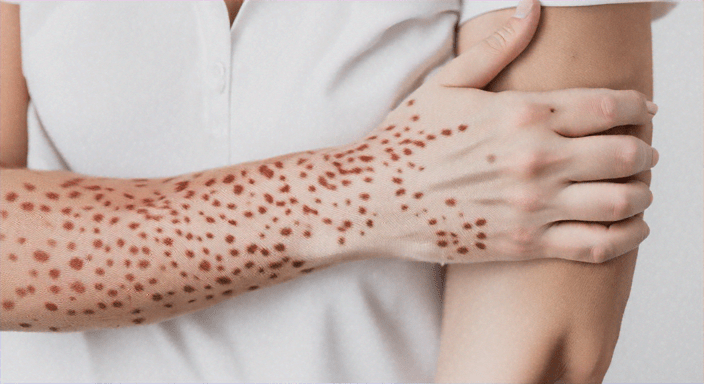
Understanding Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis, the predominant form of psoriasis, impacts approximately 80-90% of individuals afflicted with the condition. This manifestation arises when the immune system erroneously targets healthy skin cells, prompting their rapid multiplication. Consequently, this leads to an accumulation of skin cells, resulting in the formation of plaques that may induce itchiness, pain, and occasionally, cracking and bleeding.
Exploring the Causes of Plaque Psoriasis
Although the precise cause of plaque psoriasis remains elusive, it is widely believed to stem from a confluence of genetic and environmental elements. Critical factors contributing to its development include:
-
Genetics: Psoriasis frequently exhibits a hereditary pattern. Individuals with a familial history of the condition are more susceptible to developing it.
-
Immune System: An excessively active immune system incites inflammation and accelerates skin cell turnover, culminating in plaque formation.
-
Environmental Triggers: Various factors, such as stress, skin injuries, infections, and specific medications, can either trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
Identifying Symptoms of Plaque Psoriasis
The hallmark symptoms of plaque psoriasis encompass:
-
Red Patches: Elevated, inflamed patches of skin adorned with silvery-white scales. These plaques can emerge on any part of the body but are predominantly observed on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
-
Itching and Pain: Plaques may induce itchiness and discomfort, occasionally resulting in cracked and bleeding skin.
-
Dry Skin: Affected regions may become parched and exhibit peeling or flaking.
-
Joint Pain: Some psoriasis sufferers also develop psoriatic arthritis, characterized by joint pain and swelling.
Nail Changes: Psoriasis can impact the nails, leading to pitting, discoloration, and detachment from the nail bed.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
The diagnosis of plaque psoriasis generally entails a physical examination coupled with a review of the patient’s medical history. In certain instances, a skin biopsy may be conducted to exclude other conditions. Treatment strategies are designed to mitigate inflammation, decelerate skin cell production, and manage symptoms. Common therapeutic options include:
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments applied directly to the skin can alleviate inflammation and curb skin cell turnover. Typical topical treatments encompass corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and retinoids.
-
Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can aid in reducing psoriasis symptoms. Phototherapy is frequently employed when topical treatments prove ineffective.
-
Systemic Medications: For moderate to severe psoriasis, systemic medications—oral or injectable—that influence the entire body may be prescribed. These include biologics, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, circumventing triggers, and adhering to a balanced diet can assist in symptom management and enhance overall well-being.
Navigating Life with Plaque Psoriasis
Although living with plaque psoriasis presents challenges, effective management is achievable with the appropriate treatment and support. Consider the following tips for thriving with psoriasis:
-
Adhere to Your Treatment Regimen: Consistent utilization of prescribed treatments can help maintain symptom control.
-
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about psoriasis and remain abreast of new treatments and research advancements.
-
Seek Support: Joining a support group or connecting with others who have psoriasis can offer emotional support and practical advice.
-
Maintain Open Communication with Your Healthcare Provider: Regular consultations and transparent dialogue with your healthcare provider can ensure the efficacy of your treatment plan and facilitate necessary adjustments.
Concluding Remarks
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic condition necessitating continuous management. By comprehending its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with psoriasis can adopt proactive measures to manage their condition and enhance their quality of life. Consulting healthcare providers and staying informed about advancements in psoriasis care are pivotal for effective management.